- Articles ›
- Operations and IT ›
- Toyota Production System - The Origin of Operations Management Articles
Toyota Production System - The Origin of Operations Management
Toyota Production System (TPS) is one of the most productive, efficient and beautiful management systems ever designed. TPS is a socio technical system developed by Toyota which integrates theory with practice.

TPS is one of the most successful production system (or methodology). TPS gave us the terms like Lean Manufacturing, Just in Time, Kaizen etc.
TPS revolves around three basic terms
1) Muri
2) Mura
3) Muda
These 3 are Japanese terms which can be understood in the next line. The main objectives of the TPS are to design out overburden (muri) and inconsistency (mura), and to eliminate waste (muda). One of the main objectives of TPS was to reduce Muda, the waste. In order to achieve that, muri and mura needs to be eliminated from the system. There are 7 types of muda (waste) that are identified in TPS
MUDA
1. over-production
2. motion (of operator or machine)
3. waiting (of operator or machine)
4. conveyance
5. processing itself
6. inventory (raw material)
7. correction (rework and scrap)
TPS is based on two pillars,Just in time and Jidoka and is illustrated as in the image below.
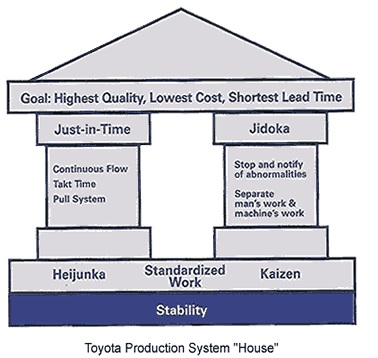
So the main objectives of TPS are
1) to reduce waste
2) To have minimal inventory through JIT
3) To have lean manufacturing system
This article can’t cover the whole scope of TPS but it gives the basic idea about it. Please find below the main systems and terms involved with TPS
Terms
1) Andon :It basically is a notification system in TPS. The centerpiece is a signboard incorporating signal lights to indicate which workstation has the problem. The alert can be activated manually by a worker using a pull cord or button, or may be activated automatically by the production equipment itself. It was based on a pull system where in the problem can be notified as it happens and then it can be corrected immediately.
2) Jidoka : It may be described as "intelligent automation" or "automation with a human touch. At Toyota this usually means that if an abnormal situation arises the machine stops and the worker will stop the production line. Automation prevents the production of defective products, eliminates overproduction and focuses attention on understanding the problem and ensuring that it never recurs.
3) Kanban : Kanban is one means through which JIT is achieved. Kanban basically is a scheduling system telling you what, when and how much to produce.
4) JIT : Just-in-time (JIT) is an inventory strategy that strives to improve a business's return on investment by reducing in-process inventory and associated carrying costs.
5) Kaizen : Kaizen refers to philosophy or practices that focus upon continuous improvement of processes in manufacturing, engineering, supporting business processes, and management.
The article has been authored by the editorial team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
If you are interested in writing articles for us, Submit Here
Share this Page on:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
All Business Sections
Write for Us