- Business Concepts ›
- Marketing and Strategy ›
- Price Structure
Price Structure
This article explains definition, importance, types & factors of Price Structure from marketing perspective.
Price Structure Definition
Price structure is a strategy where a company decides the price of its products and services. Price structure defines various prices and also discounts & offers which are consistent with the organization goals and strategy. There are various ways in a company can create price structures for its products & services.
Importance of Price Structure
Price structure can affect how company grows and is perceived by the customers. It directly affects not only the bottom line but also makes the brand image and perception. For every company, identifying the best price structure is important. A company needs to find the right balance in being competitive, highlighting the best value & getting maximum profit. A company can have low & aggressive price structure for its products & services for mass products like telecom plans & packs. Similarly, high price strategy with product quality can be a good example like Apple does. There are many pricing strategies that can be used to define the price structure.
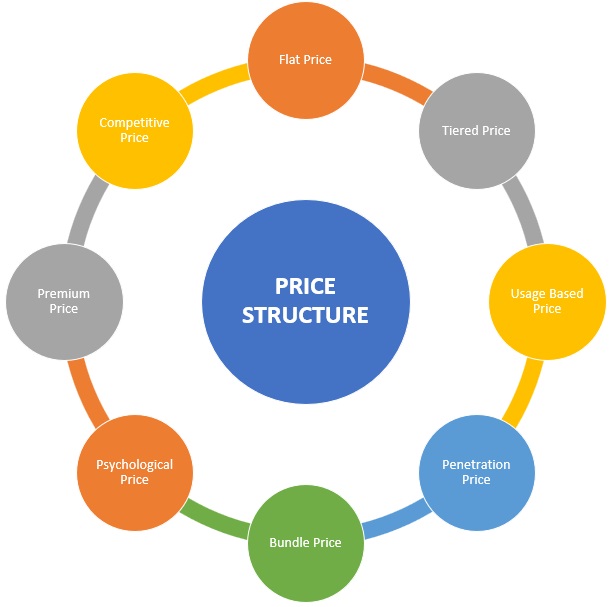
Types of Price Structures
Some of most important price structures adopted by companies are as follows.
Flat Price
A few companies or individuals might charge a flat rate for their products or services. A lawyer might have a fixed price structure based on the number of hours they provide a service. Similarly, baby-sitters, mechanics, plumbers etc have fixed rates for their service based on hours.
Tiered Price
Depending upon the additional benefits for the same service, companies can create a tiered price structure. As and more features or benefits increase, the price also increases. Airline prices are best example of tiered pricing where prices increase from economy, premium economy to business class & first class.
Usage Based Price
This price structure, known as pay per use, is a price which is defined by the number of services undertaken. A TV channel subscription is always pay per use where the more channels a user subscribes to, the more they pay. Similarly utility bills like electricity & gas are also usage based price structure.
Penetration Price
This price structure is when a company offers a very cheap price compared to competitors to penetrate a market. Companies usually take a financial hit with this strategy, and increase the price later on to regain profit once they have a strong customer base.
Bundle Price
In bundle price structure strategy, two or more products & services are bundled together and a combined price is offered. Sometimes a company can offer a soap bundled with shampoo or coffee is bundled with milk etc and this way a company is able to sell two products together, and the customer gets a slightly good deal buying bundled products.
Psychological Pricing
In this price structure, a company creates prices which appear to be less psychologically, but does not impact business. Prices such as $9.99 or $199 etc. appear to be more affordable as compared to $10 or $200 respectively.
Premium Price
There are certain brands which want to position themselves as a luxury & premium brand, and hence they use a premium price structure. These are the brands which want to promote their exclusivity as well as high product quality. Brands like Chanel, Dior, Cartier, Rolls Royce, Ferrari etc. are examples of premium pricing.
Competitive Price
Sometimes companies have to take competitors head-on with similar products & services. Higher prices would lead to lesser customers and lower prices would lead to loss of margins. Hence, competitive price structure can lead to price-matching between competitors.
Factors Affecting Price Structure
The key factors which can be useful in creating a price structure are
1. Understanding target audience & customer needs.
2. Product positioning after market research can help understand the price structure.
3. Competitor benchmarking can help understand the pricing based on similar products & services.
4. A company should always understand their own product value which finalizing a price structure.
5. Simple pricing is always good for customers to understand.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Price Structure along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us