- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Quality Control
Quality Control
Definition, Importance, Process & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Quality Control from operations perspective.
What is meant by Quality Control?
Quality control is a procedure with well defined steps implemented and executed by organizations to make sure that their product or service is governed by certain quality standards, thresholds, limits and guidelines. This activity enables firms to have a minimum threshold for its products, processes & services in terms of quality. Quality control ensures its products are high quality & cost effective, with less wastage, and giving customer a high satisfaction.
If a product doesn't meet a quality standard for a customer, they would not buy it. Also to differentiate and establish a product in the market, quality is one of the foremost parameter hence is needed to be controlled.
Importance of Quality Control
Quality control is the ultimate aim of an efficient business. Any product or service which is produced as to be at a certain quality level which a business strives for.
Customers always seek high value & good quality in the products & services that they pay for. Thus it becomes critical for companies to deliver high performance goods. This is why concepts like total quality management are used to ensure high quality finished goods.
Companies use quality control as a mechanism to have standard operating procedures with minimum levels of quality. Improvement in processes, reduction in wastage, streamlined timelines, training of workers etc. all form a part of quality control.
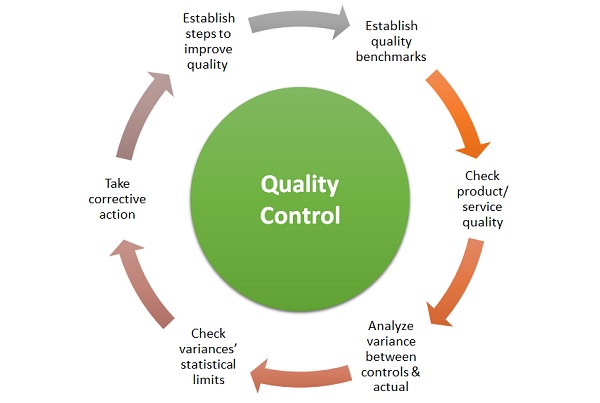
Quality Control Process
The steps to control product & process quality involves:
1. Establish controls
Establishment of specific set of controls to which product and service quality are to conform. These should be properly defined and documented so that there is no issue in understanding and implementing them. The development and the quality department should both be aligned with the controls before the production or development begins.
2. Test and check the Product/service
Checking product or service quality is very important even if the manufacturing was done as per defined controls. The testing includes testing the product or service as a whole and as modules to make sure to cover as many scenarios as possible.
3. Analyze Variance
Analyzing variances between set controls and actual quality. Ideally there should not be any variances but if there are then they should be well analyzed and documented to make sure that right numbers are there and the extent of quality issues can be assessed.
4. Check and Define Limits
There should be proper checking as to whether the variances are within statistical limits. These are defined as tolerance levels.
The tolerance can be defined at e.g. 5% or 10%. If the quality variances are within these limits then the variances are documented but no action is taken.
5. Corrective Decisioning
If the variances are way over the tolerance limits then a corrective action and decision has to be taken for sure. Either it can be rejecting a batch or sending them back for rework to improve the overall quality.
The entire process would be repeated to make sure that no product of inferior quality reaches the customers.
6. Benchmark and Feedback
This includes establishing procedures so that the variances do not arise again. Quality control is an ongoing process which keeps improving in every development cycle. These quality data and feedback should all be properly analyzed and looped back in quality control definition step to ensure that the next time, the quality is even higher within the budgetary limits though.
Quality control attaches immense importance to statistical procedures as it these procedures that lend quantitative authenticity to statistical controls.
Quality Control Methods
Broadly there are 2 quality control methods in modern business:
1. Automated & Statistical
This method focusses on automating the entire manufacturing process in which there is a constant monitoring of quality control limits and thresholds against the manufactured products. Statistical methods and systems are used to evaluate the actual product data with control limits and a real time view of the quality is created through charts and various methods like x-bar chart, pareto etc.
These days with robotics coming up in every process, the quality control can be entirely done by the robotics through machine vision and analysis. The automated quality control systems can monitor, control and improve the overall development process in real time. This ensure the highest level of quality.
2. Manual Sampling Driven
In many business, the method of sampling and inspection is used where a random sample is taken from the inventory of almost finished goods and are manually inspected by the quality assurance department. If the sample is within the quality control limits then the entire batch is passed else corrective actions and decisions have to be considered.
Discarding the entire batch can be one of the decisions if the variances are very high.
Difference between Quality Control and Quality Assurance
These both concepts are quite interlinked but there is a difference. They both form part of the overall quality process and system in an organization. The quality control is more related to the definition and documentation of certain quality limits and thresholds which can be used for testing, research, development and overall mindset of the company.
But the quality assurance is the overall execution and inspection of the produced goods and services against the limits set by the quality control.
Both the quality control and quality assurance complement each other and makes sure that the company can product highest quality products and services which match the customer requirements as much as possible.
Example of Quality Control
A very famous example of quality control is that of Toyota. The company has adopted a system of Total Quality Management wherein it embraces statistical methods of Quality control and Quality management to ensure its products conform to all specified controls and procedures and are of utmost good quality.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Quality Control along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us