- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Distribution Channel Management
Distribution Channel Management
This article explains definition, importance, types & example of Distribution Channel Management from operations perspective.
Distribution Channel Management Definition
Distribution channel management is process of managing transfer of products from producer to end customer. Distribution channel is the medium or channel which companies use to carry products. It is a critical element in business as this process is used to distribute products to retailers & customers across various locations.
Importance of Distribution Channel Management
Every company produces a large volume of goods which are made for customers which are spread across geographies. While goods are produced in a factory, it is critical to understand how these goods are to be sent out to warehouses, distributors, retailers and eventually customers spread across locations. This is where distribution channel management is essential in ensuring an efficient, cost-effective, profitable & secure distribution of products.
Types of Distribution Channel
It is subdivided into 2 categories:
1. Direct Channel: The seller/supplier directly sells the product to the customer in direct channel. He himself choose the medium; be it ecommerce or through stores. It requires hiring of few sales people or building operations for ecommerce website.
2. Indirect Channel: A specialized intermediary is added in this type of channel as they have the required contacts, experience and scale of operations. He might be a consultant, Original Equipment manufacturer (OEMs), etc. The reason for this includes the efficiency of distribution costs.
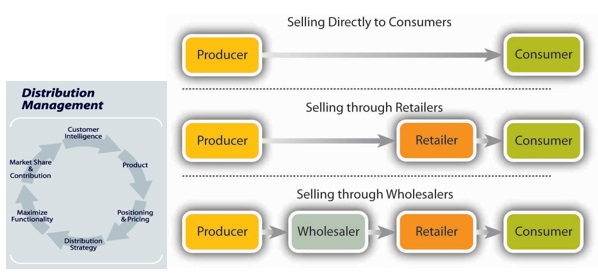
Characteristics of Distribution Channel Management
Some of the main elements of an effective distribution channel management are:
1. Route: The most preferred route has to be selected depending on geography, locations, cost etc.
2. Flow: The flow of goods & services has to be addressed in a structured, systematic & sequential manner, for a smooth execution.
3. Logistics: The selection of the type of logistics medium like rail, road, airways, waterways, pipeline etc.
4. Levels: The different levels or intermediaries have to be finalized like wholesalers, retailers, agents etc.
Example
Consider a smartphone manufacturing company, which wants to sell its phones. The company can use multiple distribution channels to ensure its phones are sold across various geographies & customers. The company can distribute its phones though its own stores, through multi-brand retail outlets & even ecommerce platforms. As a part of its strategy, the company will have to tie-up with intermediaries like distributors, wholesalers, retailers etc.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Distribution Channel Management along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us