- Business Concepts ›
- Human Resources (HR) ›
- Organizational Structure
Organizational Structure
Definition, Importance & Types
This article covers meaning & overview of Organizational Structure from HRM perspective.
What is meant by Organizational Structure?
Organizational structure is the framework on how employees work based on their duties & positions. Organizational structure, which is predominantly a hierarchy of the employees and the functions, is essential in order to streamline operations and processes within an organization. This is a critical part of a company as it defines the flow of work, accountability & authority to take decisions.
Importance of Organizational Structure
There are many functions in a company, who have to work together to achieve the goal of the business. Every function needs to have different people with varied skill sets to grow the business. To ensure that there is flow of information & work, employees have defined roles & responsibilities, companies have a framework. This is known as organizational structure. By doing this, the hierarchy, roles, positions, duties, decision making abilities of all employees are well defined.
An organizational structure usually starts with the CEO at the apex of the company. Below that there are vertical or functional leads for different departments like marketing, finance, HR, operations, IT, admin etc. All these report to the CEO. Below each lead, there are other employees who have expertise in that particular field. Thus, an organizational structure is a pyramid like framework, connecting all employees on the basis of their job profile. Organizational structure departmentalization can be created based on functions, geography, product, customer & process.
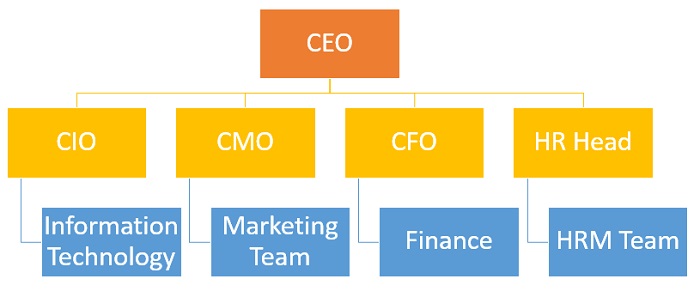
The above image shows a typical organizational structure.
Read More
Features of Organizational Structure
Some of the main elements of having an organizational structure are:
1. Clearly defines roles, responsibilities, position & decision-making power of an employee.
2. Defines the flow of communication & work.
3. Divides work on the basis of functions & skills sets.
4. Establishes a line of authority & flow of delegation.
5. Defines a clear path of interaction between different departments.
Organizational structure is also critical to delegate work & monitor teams as each job profiles work is defined.
Types of Organizational Structure
The popular organisational structures include:
Functional Structure: In this case, the organisation is divided into segments based on the functions performed by the employees. This helps to increase efficiency in each function. It is generally used in large organizations.
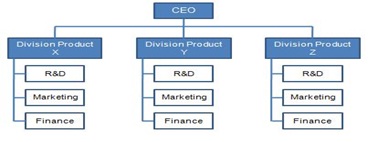
Divisional Structure: In this case, the organisation is divided into divisions which could be based on the product, Markets or Geographic area. Each division has its own set of functions like finance, marketing etc., like small micro organizations within one large organisation.
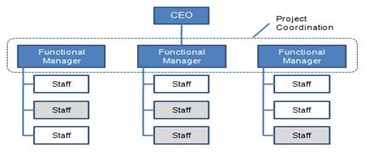
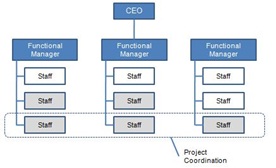
Matrix: The matrix structure is typically a hybrid version of both the functional and divisional structures.
Pre-Bureaucratic: Found in startups, No standards with a centralised structure and usually one decision maker.
Bureaucratic: Standardized structures and suitable for large organizations.
Post-Bureaucratic: Follow strict hierarchies but open to modern ideas and methodologies.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Organizational Structure along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us