- Business Concepts ›
- Operations and Supply Chain ›
- Job Production
Job Production
Definition, Importance & Example
This article covers meaning & overview of Job Production from operations perspective.
What is meant by Job Production?
Job production is a manufacturing process which involves workers making a single unique customized product for a single customer. Depending upon the customer needs, job production method is used to create a product from start to finish. This method of production is not used for producing goods in mass quantity.
Importance of Job Production
Job production is an important concept in manufacturing. It is driven by exact need or requirements of a customer. Depending upon the need, the team of workers produce the product or goods specifically for the customer. Job production basically focuses on low volume of production but offers a higher variety of the finished product.
These specialized made to order to engineer to order products can lead better products for the customer and better opportunity for the manufacturer.
Read More
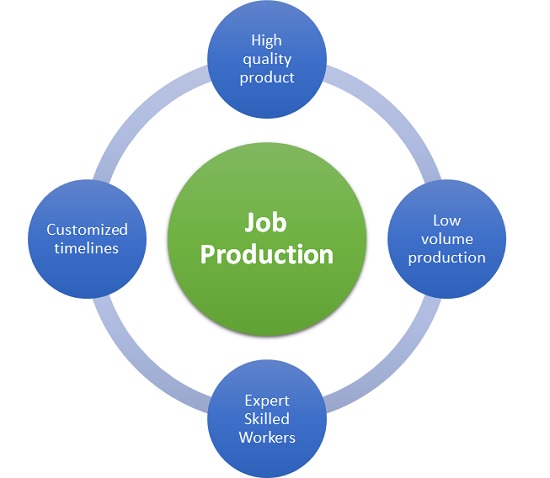
Characteristics of Job Production
Manufacturing goods or products based on this method is characterized by the following features:
1. Low production volume
Job production focuses on delivering goods for one customer at a time.
2. Varied timelines
Since the product is dependent on individual customer needs, there is no fixed time in completion of the product.
3. Highly skilled workers
Since the product has to be customized, the workers need to have special skills & expertise to carry out job production.
4. Detailed planning
As compared to mass or batch production, where you can plan once, job production requires planning as per the customer order received.
Examples of Job Production
Some examples of job production, to create customized products for customers are:
1. Building construction is a job production where each building has a different architecture, design, landscape, geography, investments, materials etc.
2. Creating customized clothes like wedding gowns, tuxedos require custom planning, design & execution, and uses expertise of tailors to stitch these special clothes.
3. Jewellery items like necklaces, bracelets, rings etc. are often customized using special designs, metals, gems etc.
All these examples above show the use of job production to manufacture niche products.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Job Production
Some advantages of this method of manufacturing are:
1. Higher quality of finished product.
2. Customizations can be done based on exact customer requirement.
3. Higher customer satisfaction for a high quality product.
4. Because of expertise of skilled workers, companies can charge higher for job production.
Some drawbacks of job production are:
1. Higher cost of production.
2. Requires special planning every time a new customer comes.
3. Very slow volumes of production.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Job Production along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team. The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
What is MBA Skool?About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
Quizzes & Skills
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
All Business Sections
Write for Us